本文共 3037 字,大约阅读时间需要 10 分钟。
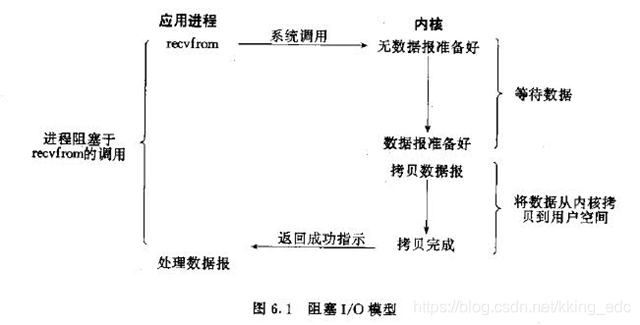
一、阻塞IO模型
最传统的一种IO模型,即在读写数据过程中会发生阻塞现象。
当用户线程发出IO请求之后,内核会去查看数据是否就绪,如果没有就绪就会等待数据就绪,而用户线程就会处于阻塞状态,用户线程交出CPU。当数据就绪之后,内核会将数据拷贝到用户线程,并返回结果给用户线程,用户线程才解除block状态。
典型的阻塞IO模型的例子为:
data=socket.read()
如果数据没有就绪,就会一直阻塞在read方法。
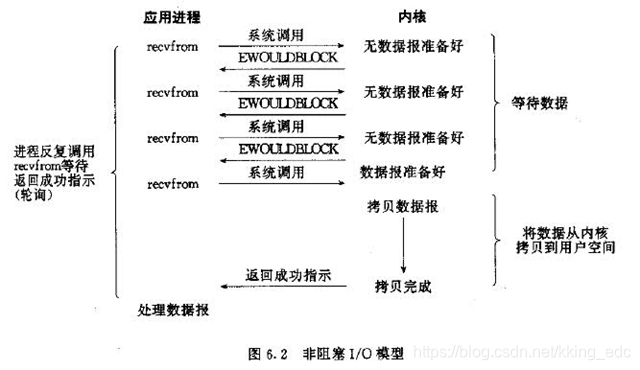
二、非阻塞IO模型
当用户线程发起一个read操作后,并不需要等待,而是马上就得到了一个结果。如果结果是一个error时,它就知道数据还没有准备好,于是它可以再次发送read操作。一旦内核中的数据准备好了,并且又再次收到了用户线程的请求,那么它马上就将数据拷贝到了用户线程,然后返回。
所以事实上,在非阻塞IO模型中,用户线程需要不断地询问内核数据是否就绪,也就说非阻塞IO不会交出CPU,而会一直占用CPU。
典型的非阻塞IO模型一般如下:
while(true){ data = socket.read(); if(data!= error){ 处理数据 break; }} 但是对于非阻塞IO就有一个非常严重的问题,在while循环中需要不断地去询问内核数据是否就绪,这样会导致CPU占用率非常高,因此一般情况下很少使用while循环这种方式来读取数据。
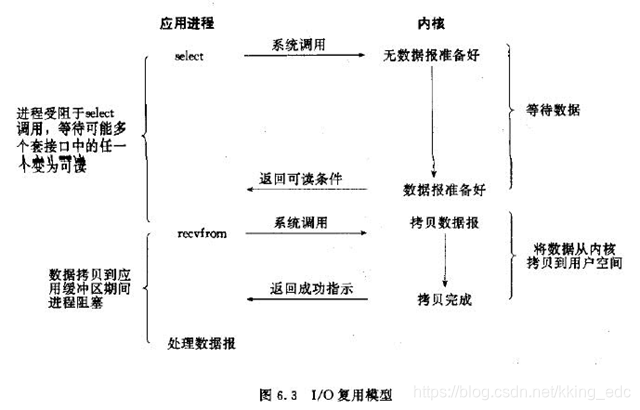
三、多路复用IO模型
多路复用IO模型是目前使用得比较多的模型。Java NIO实际上就是多路复用IO。
在多路复用IO模型中,会有一个线程不断去轮询多个socket的状态,只有当socket真正有读写事件时,才真正调用实际的IO读写操作。因为在多路复用IO模型中,只需要使用一个线程就可以管理多个socket,系统不需要建立新的进程或者线程,也不必维护这些线程和进程,并且只有在真正有socket读写事件进行时,才会使用IO资源,所以它大大减少了资源占用。
在Java NIO中,是通过selector.select()去查询每个通道是否有到达事件,如果没有事件,则一直阻塞在那里,因此这种方式会导致用户线程的阻塞。
也许有朋友会说,我可以采用多线程+ 阻塞IO 达到类似的效果,但是由于在多线程 + 阻塞IO 中,每个socket对应一个线程,这样会造成很大的资源占用,并且尤其是对于长连接来说,线程的资源一直不会释放,如果后面陆续有很多连接的话,就会造成性能上的瓶颈。
而多路复用IO模式,通过一个线程就可以管理多个socket,只有当socket真正有读写事件发生才会占用资源来进行实际的读写操作。因此,多路复用IO比较适合连接数比较多的情况。
另外多路复用IO为何比非阻塞IO模型的效率高是因为在非阻塞IO中,不断地询问socket状态是通过用户线程去进行的,而在多路复用IO中,轮询每个socket状态是内核在进行的,这个效率要比用户线程要高的多。
不过要注意的是,多路复用IO模型是通过轮询的方式来检测是否有事件到达,并且对到达的事件逐一进行响应。因此对于多路复用IO模型来说,一旦事件响应体很大,那么就会导致后续的事件迟迟得不到处理,并且会影响新的事件轮询。
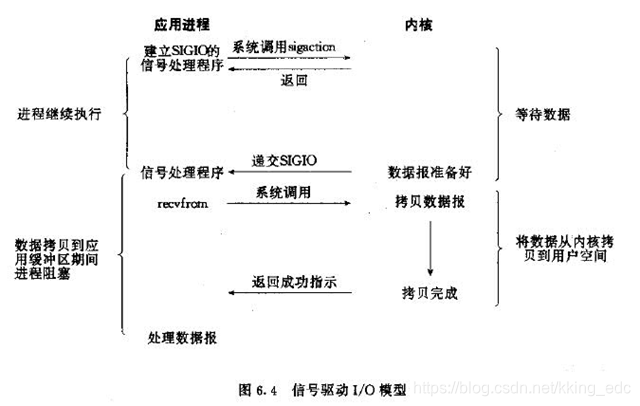
四、信号驱动IO模型
在信号驱动IO模型中,当用户线程发起一个IO请求操作,会给对应的socket注册一个信号函数,然后用户线程会继续执行,当内核数据就绪时会发送一个信号给用户线程,用户线程接收到信号之后,便在信号函数中调用IO读写操作来进行实际的IO请求操作。这个一般用于UDP中,对TCP套接口几乎是没用的,原因是该信号产生得过于频繁,并且该信号的出现并没有告诉我们发生了什么事情
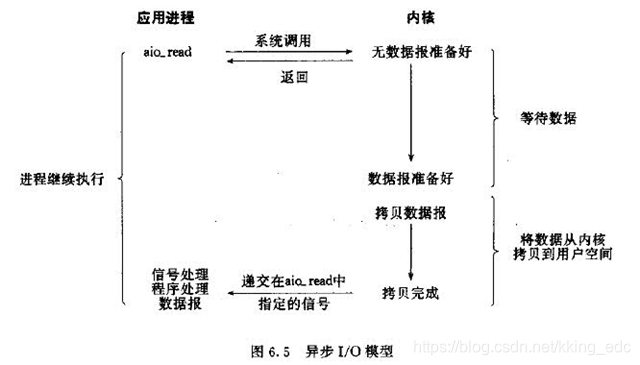
五、异步IO模型
异步IO模型才是最理想的IO模型,在异步IO模型中,当用户线程发起read操作之后,立刻就可以开始去做其它的事。而另一方面,从内核的角度,当它受到一个asynchronous read之后,它会立刻返回,说明read请求已经成功发起了,因此不会对用户线程产生任何block。然后,内核会等待数据准备完成,然后将数据拷贝到用户线程,当这一切都完成之后,内核会给用户线程发送一个信号,告诉它read操作完成了。也就说用户线程完全不需要关心实际的整个IO操作是如何进行的,只需要先发起一个请求,当接收内核返回的成功信号时表示IO操作已经完成,可以直接去使用数据了。
也就说在异步IO模型中,IO操作的两个阶段都不会阻塞用户线程,这两个阶段都是由内核自动完成,然后发送一个信号告知用户线程操作已完成。用户线程中不需要再次调用IO函数进行具体的读写。这点是和信号驱动模型有所不同的,在信号驱动模型中,当用户线程接收到信号表示数据已经就绪,然后需要用户线程调用IO函数进行实际的读写操作;而在异步IO模型中,收到信号表示IO操作已经完成,不需要再在用户线程中调用iO函数进行实际的读写操作。
注意,异步IO是需要操作系统的底层支持,在Java 7中,提供了Asynchronous IO。简称AIO
前面四种IO模型实际上都属于同步IO,只有最后一种是真正的异步IO,因为无论是多路复用IO还是信号驱动模型,IO操作的第2个阶段都会引起用户线程阻塞,也就是内核进行数据拷贝的过程都会让用户线程阻塞。
六、两种高性能IO设计模式
在传统的网络服务设计模式中,有两种比较经典的模式:
一种是多线程,一种是线程池。 对于多线程模式,也就说来了client,服务器就会新建一个线程来处理该client的读写事件,如下图所示: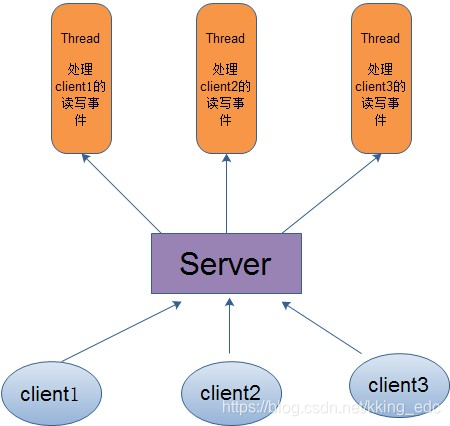
因此,为了解决这种一个线程对应一个客户端模式带来的问题,提出了采用线程池的方式,也就说创建一个固定大小的线程池,来一个客户端,就从线程池取一个空闲线程来处理,当客户端处理完读写操作之后,就交出对线程的占用。因此这样就避免为每一个客户端都要创建线程带来的资源浪费,使得线程可以重用。
但是线程池也有它的弊端,如果连接大多是长连接,因此可能会导致在一段时间内,线程池中的线程都被占用,那么当再有用户请求连接时,由于没有可用的空闲线程来处理,就会导致客户端连接失败,从而影响用户体验。因此,线程池比较适合大量的短连接应用。
因此便出现了下面的两种高性能IO设计模式:Reactor和Proactor。
在Reactor模式中,会先对每个client注册感兴趣的事件,然后有一个线程专门去轮询每个client是否有事件发生,当有事件发生时,便顺序处理每个事件,当所有事件处理完之后,便再转去继续轮询,如下图所示:
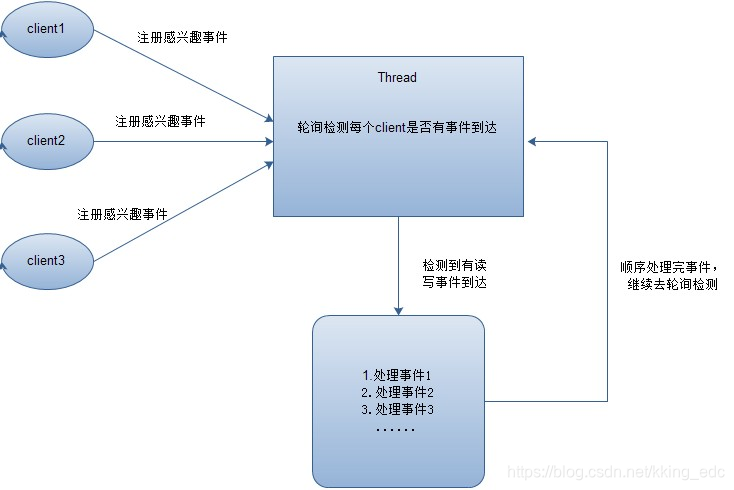 从这里可以看出,上面的五种IO模型中的多路复用IO就是采用Reactor模式。注意,上面的图中展示的 是顺序处理每个事件,当然为了提高事件处理速度,可以通过多线程或者线程池的方式来处理事件。Java NIO使用的就是这种
从这里可以看出,上面的五种IO模型中的多路复用IO就是采用Reactor模式。注意,上面的图中展示的 是顺序处理每个事件,当然为了提高事件处理速度,可以通过多线程或者线程池的方式来处理事件。Java NIO使用的就是这种 在Proactor模式中,当检测到有事件发生时,会新起一个异步操作,然后交由内核线程去处理,当内核线程完成IO操作之后,发送一个通知告知操作已完成,可以得知,异步IO模型采用的就是Proactor模式。Java AIO使用的这种。
转载地址:http://mbtx.baihongyu.com/